དངུལ་རྩིས་ལྷན་ཁག། དཔལ་ལྡན་འབྲུག་གཞུང་།
Ministry of Finance
Royal Government of Bhutan
Office of the Secretary
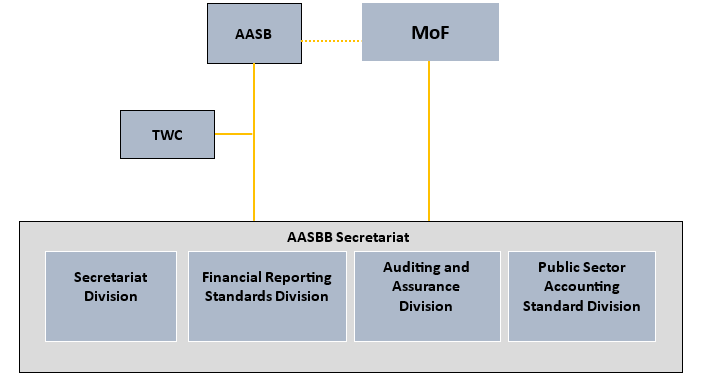
Accounting and Auditing Standard Boards of Bhutan
Accounting and Auditing Standard Boards of Bhutan
About the Department
Mission
To enhance financial reporting, auditing standards, and professionalism through governance, capacity building and institutional support fostering transparency and economic stability across all sectors.
Vision
The leading agency in setting internationally recognized financial and auditing standards ensuring transparency, efficiency and accountability in Bhutan’s financial ecosystem.
Objectives
- To Adopt Bhutanese Accounting Standards (BAS) in line with International Accounting Standards (IAS)/International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Review, update and issue Bhutanese Accounting Standards and International Public Sector Accounting Standards.
- Adopt and implement International Standards on Auditing (ISA).
- Recommend new standards/amendments in BAS, IPSAS and ISA.
- Harmonize the statutory and legal framework requirements of BAS and ISA with other relevant legislation.
1. Financial Reporting Standards Division
- Review and issuance of new standards or amendments to standards (BAS & BAS for SMEs)
- Compliance Review (BAS & BAS for SMEs
- Provide Technical clarifications (BAS & BAS for SMEs)
- Support for professional development (BAS & BAS for SMEs)
2. Public Sector Accounting Standards Division
- Review and issuance of new standards or amendments to standards (Public sector Accounting Standards).
- Compliance Review.
- Provide Technical clarifications
3. Auditing & Assurance Standards Division
- Review and issuance of new standards or amendments to standards (ISA).
- Quality Assurance (ISA).
- Providing Technical clarification (ISA).
- Facilitate establishment of Institute of Chartered Accountants of Bhutan.
4. Administration and Finance Division
Discharge of Administrative and Finance functions
- Accounting and Budgeting.
- Administration.
- Project management.
- TWC and Board meeting.
- Support for In-house professional development.
Our Links
Organogram
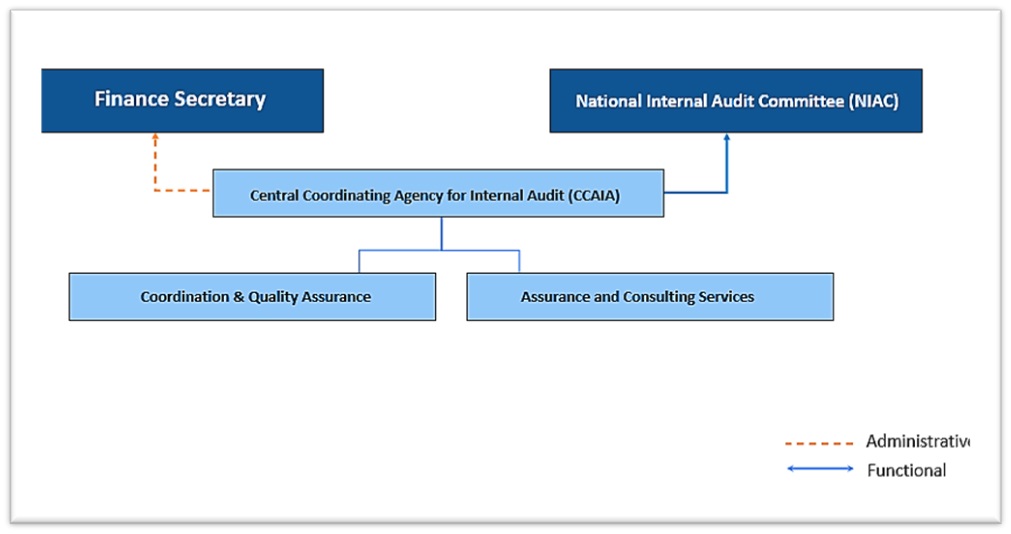
Central Coordinating Agency for Internal Audit
Central Coordinating Agency for Internal Audit (CCAIA)
About Us
The National Internal Audit Committee comprises of the following members:
- Hon’ble Cabinet Secretary – Chairperson
- Secretary, Ministry of Finance – Member
- Director, RCSC – Member
- Chief Internal Auditor, CCAIA – Member Secretary
Definition of Internal Auditing
As per the Global Internal Audit Standards issued by the Institute of Internal Audit (IIA), USA:
“Internal auditing is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations. It helps an organization accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes.”
Based on the IIA definition, the RGoB has accordingly defined the purpose of the Internal Audit in the Internal Audit Charter as:
“The Internal Audit Services conduct audits and reviews, using a systematic and disciplined
approach, to provide:
(i) Independent and objective assurance on the efficiency and effectiveness of their respective
Entity’s governance, risk management, control, and accountability processes.
(ii) Recommendations for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the
Entity’s operations, achieving organizational objectives, and proper stewardship of
resources.
Mission
Core Values
- The CCAIA reports administratively to the Finance Secretary and functionally to the chairperson of the National Internal Audit Committee.
- In line with Section 23 (O) of the Public Finance Act of Bhutan 2007, the Central Coordinating Agency under the Ministry of Finance has the following core mandates
Coordination and Quality Assurance:
- Coordinate the overall Internal Audit functions;
- Ensure quality assurance and improvement, uniformity and consistency of Internal Audit function;
- Prepare and issue periodic reports summarizing results of audit activities and the status of implementation of past audit recommendations to the National Internal Audit Committee and share a copy with the respective management for actions;
- Develop, review, and modify the Charter, Standards, Manuals, and Code of Ethics from time to time;
- Render technical backstopping and consultation to the Internal Auditors as and when required;
- Promote functional partnerships with the Royal Audit Authority, the Anti-Corruption Commission, and other relevant law enforcement agencies;
- Promote understanding, acceptance, and utilization of Internal Audit services by all levels of Management;
- Develop professional proficiency through enhancement of skills, techniques, and knowledge of Internal Auditors;
- Coordinate recruitments, transfers, promotions and develop career paths for Internal Auditors;
- Provide guidelines to Internal Auditors and ensure professional practice of Internal Audit;
- Protect Internal Auditors from undue reprisals for their professional conduct;
- Liaise with other national, regional, and international bodies for the development of Internal Audit Services in the country;
- Provide secretarial support to the National Internal Audit Committee which is the ultimate appellate body to the Internal Audit function in the country.
Assurance and Consulting Service:
- Develop an annual audit plan based on comprehensive risk assessment in consultation with the agencies and submit it to the National Internal Audit Committee for approval;
- Implement the approved annual audit plan following the Standards for Professional Practice of Internal Auditing, Charter, Internal Audit Manual, and the Internal Audit’s Code of Ethics;
- Provide advisory services for assignments/reviews requested by the agencies.
- Communicate the impact of resource limitations and significant interim changes in the plan;
- Issue reports annually summarizing results of audit activities and status of implementation of past audit recommendations to the management;
- Provide adequate follow-up to ensure corrective action is taken and report its status to the National Internal Audit Committee;
- Consider the scope of work of the external auditors and other regulators as appropriate and collaborate with them to provide optimal coverage and avoid duplication of work.
Organogram
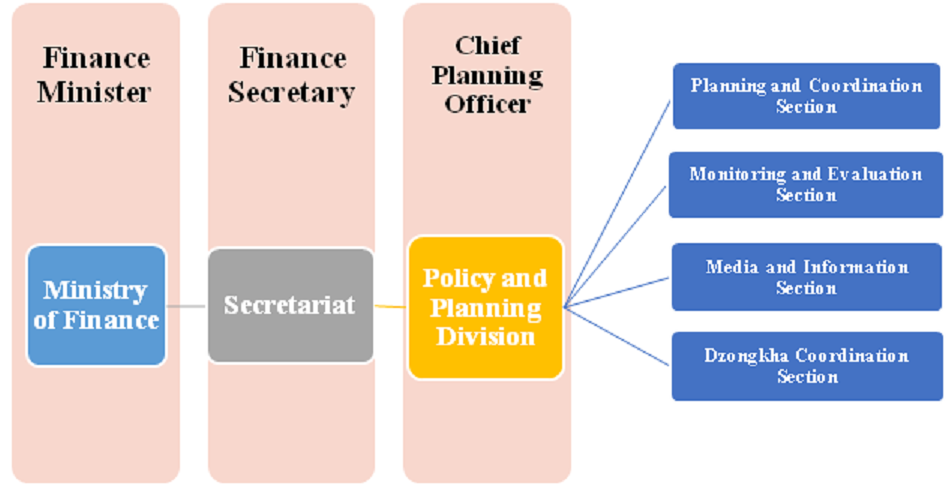
Policy & Planning Division (PPD)
Policy & Planning Division (PPD)
The Policy and Planning Division is the policy arm of the Ministry. The PPD is the focal for coordinating and spearheading policy and plan formulation and setting the targets ofofthe Ministry. This is to ensure the responsibilities of the Departments/Divisions are in line with the Vision of the Ministry and that of the National Objectives.
Policy Coordination and Planning Section
This Section is responsible for developing Plans, Programmes and Projects of the Ministry. The Section undertakes research and policy analysis to ensure coherence and consistency in the policies, socio-economic development objectives, and programs. The Section also coordinates Projects, if any to be implemented by various Departments under the Ministry.
This Section is also responsible for coordinating MoF’s interaction with the Cabinet and through the Cabinet with the Parliament. It also facilitates and liaison between the external stakeholders and within the Departments/Divisions of the Ministry.
All Policy issues and decisions are carried out through the Policy & Planning Coordination Meeting (PPCM) chaired by Hon’ble Minister and this Section is responsible for the coordination and implementation of the decisions of the PPCM.
One of the most important responsibilities of the Section is to spearhead the preparation of Annual Budget which the Hon’ble Minister presents to the Parliament. The Section will also spearhead major reforms and initiatives of the Government.

Monitoring and Evaluation Section
This Section is responsible for reviewing the policies and legislations that require comments and views of the Ministry of Finance. The Section is responsible for representing Ministry of Finance in the relevant national and international organizations.
The section is also responsible for mid-year reviews of the Ministry’s annual plans and the Mid-Term Review of the Five Year Plans and the Round Table Meetings. The Section also conducts ad-hoc monitoring and evaluation exercises on relevant macro-fiscal and public finance issues in consultation with the relevant departments.
The Section is particularly responsible for the Regulatory Impact Assessment of the policies developed by the Departments/Divisions of the Ministry of Finance.
Media and Information Section
As the Media Focal of the Ministry and working under the direct supervision of the Hon’ble Minister and Secretary, this Section shall be responsible for the media and knowledge management both mainstream media and social media.
Dzongkha Coordination Section
As one of PPD’s main responsibilities is to spearhead the preparation of Annual Budget which the Hon’ble Minister presents to the Summer Session of the Parliament, the Report, Speech and Bills for submission to the Parliament have to be translated in Dzongkha. The Ministry also frequently has to translate agreements, conventions, and legislation that are submitted to the Parliamentary for ratification. This Section therefore will be responsible for translation of Report, Conventions, Legislations and any other translation assignments on behalf of the Ministry.

Advisory Support Services to the Office of Minister and Secretary
The Policy and Planning Division will also provide advisory support services to and carry out any assignments given by the Office of the Minister and Secretary.
Property Assessment and Valuation Agency (PAVA)
Property Assessment and Valuation Agency (PAVA)
In Bhutan, ongoing development across the country, including upcoming mega-hydro projects, is leading to increased property accumulation and the need for asset expropriation. To manage this effectively, a sound valuation system is essential. In response, and in line with the Land Act of Bhutan 2007, the Property Assessment and Valuation Agency (PAVA) were established in 2008 under the Ministry of Finance to assess and fix land and collateral property values.
Objectives
- Help in establishing a formalized land and property market
- Directly or indirectly help avoid/discourage land hoarding and speculation
- Facilitate in fixing land and property taxes, lease rents, compensation rates
- Facilitate streamlining of all land and property related economy under one umbrella
- To ensure uniformity and fairness in the assessment of property by providing a source of guidance on valuation/assessment of property
- To study material for research and development of real estate
- Carry out public awareness programs to increase public understanding on standard practices of valuation
Finance Division
Finance Division
- Planning and Development of Human Resources for the Ministry and Divisions
- Financial Management and Related Accounting Matters for the Entire Ministry
- Procurement/Tendering of the Office Equipments and Supplies for the Ministry
- Formulation and Interpretations of Rules
The functions and responsibilities of AFD:
Administration & Finance consists of Personnel Administration section, Finance Section, General Administration section, Procurement section, Vehicle allotment section and computer section.
Administration
Administration
Procurement
Procurement
Human Resource Division (HRD)
Human Resource Division (HRD)
Functions and Roles
The Chief Human Resource Officer heads the Human Resource Division (HRD) and it functions directly under the Directorate of Services. The core mandate of HRD is to develop long and short-term Human Resource development and management plan and employment plan of the Ministry of Finance. The Ministry parents the Procurement Officers, Finance Officers, Accounts Assistants and Internal Auditors serving in the agencies thus, the role of the HRD cuts across other line Ministries and Agencies.
Under the Ministry of Finance, there are 6 Departments including the Directorate of Services and each department is being designated with focal HRO (s) to manage and cater the services effectively and efficiently. The HRD formulates any human resource plans and policies in close collaboration with respective Departments and Divisions of the Ministry. Once the plans and programs are in place, the HR Division plays the key role in executing it in coordination with the Departments and Divisions.
Following are some of the key functions of HRD:
1. Service delivery
The following are the services broadly being delivered by HRD in line with Bhutan Civil Service Rules and Regulations 2018 (BCSR 2018):
- Recruitment, Selection and Appointment
- Trainings and capacity development
- Transfer
- Promotion
- Salary fixation and increment
Recruitment, Selection and Appointment:
The HR Division collects the manpower requisition from respective Departments and other line Ministries and Agencies. The requirement is reviewed by HR Division based on the Approved Staffing Strength approved by Royal Civil Service Commission (RCSC) in the beginning of the Five-Year Plan development. The selection is merit based, and the vacancy of the post and its requirements are announced in the media and on the Ministry’s website in a transparent manner.
Trainings and Capacity Development:
There are two types of trainings that are being carried out by HRD i.e, Long Term Training(both planned and adhoc program) and Short Term Training (STT). The planned trainings are usually the long-term trainings/study that is incorporated in the HRD Master Plan approved by RCSC. Also the adhoc trainings are carried out but are subject to the approval of the RCSC. The duration of the Adhoc training or STT ranges from few days to couple of months but not exceeding six months that include workshops, seminars and meetings exceeding five days. All trainings/studies are on merit based and equal opportunities are given to all through open competitive selection procedures. The slots are announced through media and on the website of the Ministry.
Transfer
The general transfer exercise is conducted once in a year from the month of October to November as per the transfer guidelines of the Ministry. Generally, the civil servants parented by the Ministry serving in various agencies are being transferred upon the completion of five years serving in the same agency. The transfer exercise is centrally initiated by the HRD in collaboration with the respective parent departments.
The transfers were facilitated based on the availability of posts and the reliever in their opted places. The criteria for transfer review are mainly on marital, medical and domestic ground. The individuals are given the choice of three places for posting which is then submitted to the HRD routed through the HRC of respective departments and working Agencies. The HRD then reviews and finalizes the transfer proposals in coordination with the respective parent departments which are put up to the HR Committee meeting of the Ministry for approval.
Promotion
The schedule for promotion is twice in a year i.e in January and July. The process starts from October for January promotion and from March for July promotion. The promotion is based on individual performance and every individual is eligible for promotion within the period of 4 to 5 years. The performance is assessed through Individual Work performance (IWP) or the activities that are drawn in the beginning of the financial year between the Supervisor and the individual. The IWP is usually linked with the Ministry’s goal through Division’s/Department’s outputs. The IWP scores of individuals are further moderated by the Moderation Committee in Department wise based on the APA score of the departments and the final score is awarded to the individuals. The final ratings taken from the moderation exercise are taken into consideration for the purpose of promotion.
Pay fixation and incremen
The salaries for the new recruits for the departments at the headquarters are fixed by the HRD. On the other hand, the annual increments for the employees at the HQ are granted either in January or July depending on their appointment dates by the HRD.
2. Human Resource Committee
As mandated by the BCSR 2018, every Ministry and Agency has to institute a HR Committee (HRC). The very purpose of instituting the HRC is to guide all the HR actions of the Ministry whilst promoting broader participation and ensuring fair and transparent HR decision making based on merit.
All the HR issues are put up to the HRC and the meeting is convened every forth nightly chaired by the Hon’ble Secretary of the Ministry who is the head of the Agency. The members of the committee are Directors/Director Generals of all the Departments, Chief Planning Officer from Policy and Planning Division (PPD) and the Chief Legal Officer from Legal Division. The Chief HR Officer of HRD and HROs are the member secretary to the HR Committee.
3. Staff Record and Information System
The HR information of the staff both at the Headquarter and working in the agencies are maintained through Zhiyog Electronic System (ZESt)developed by RCSC.
On the other hand, the Ministry maintains our own HR Information System (HRISOF) developed by our ICT personnel for the management of Para-regular employees under the Department of National Properties and Directorate of Services.
4. Staff Welfare Scheme
The welfare of the staff of the Ministry is taken care of by the Civil Servants’ Welfare Scheme (CSWS) of the RCSC, and this scheme applies to all the civil servants across the Ministries and Agencies. All civil servants become members of CSWS on a voluntary basis and this scheme provides the financial contribution (Semso) during the event of demise of the member or the member’s dependents.
On the other hand, there are other schemes like Civil Service Support Desk and Exit Management after superannuation which is covered under Civil Service Well-being Program initiated by RCSC. For more information, the details can be viewed from RCSC’s website at www.rcsc.gov.bt.
5. Civil Service Award
The HRD coordinates the Civil Service Award annually which was instituted by RCSC to recognize and reward civil servants for their dedicated service to the Tsa-Wa-Sum in December.
The award is given to staff with clean service records who have served the Tsa-Wa-Sum with full dedication and loyalty primarily based on the duration served in the Civil Service as follows:
- 10 years- Certificate with a Medal (Bronze)
- 20 years – Certificate with a Medal (Silver)
- 30 years- Certificate with a Medal (Gold)
- Lifetime Award- Certificate with a Medal (Gold) upon completion of the retirement age prescribed in the BCSR, 2018.
Information Communication & Technology Division (ICTD)
Information Communication & Technology Division (ICTD)
A brief mandate, roles and duties of the ICT Division are as follow:
ICT Division Duties & Responsibilities
- ICT Governance, Management and coordination (Management of all IT personnel, resources and operations of the organizations;)
- ICT Planning and Budgeting for common ICT services.
- Formulation and implementation of Information Technology and Knowledge management strategy to guide the organization’s future directions;
- Planning and coordinating of cost-effective and better-quality procurement of information technology;
- Ensures that the organization’s databases and application standards conform to the technical standards followed in the country; eGif Standard compliance.
- Manage staff training in information technology and knowledge management.
ICT Division Supports
- Support of change management practices and re-engineering initiatives related to ICT.
- Manage and support network and web services;
- Management of organization’s telecommunications network;
- Advice on and support organization’s infrastructure and applications systems.
- Support in Tender services related to ICT equipment’s/works.
Legal Division
Legal Division
Secretariat Staff
Secretariat Staff

Dasho Leki Wangmo
- Designation: Finance Secretary
- Email: lekiwangmo@mof.gov.bt

Thinlay Yangdon
Chief Programme Officer
- Email: tyangdon@mof.gov.bt