དངུལ་རྩིས་ལྷན་ཁག། དཔལ་ལྡན་འབྲུག་གཞུང་།
Ministry of Finance
Royal Government of Bhutan
Department of Macro-Fiscal and Development Finance
About Us
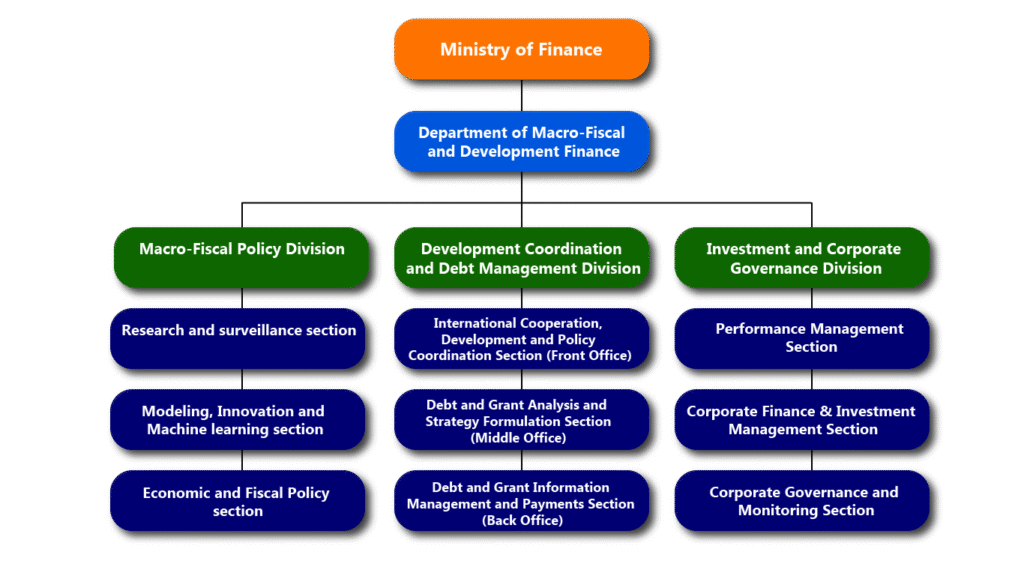
The Department of Macro-Fiscal and Development Finance (DMDF) is supported by three divisions, namely, 1) Macro-Fiscal Policy Division, 2) Development Coordination and Debt Management Division, and 3) Investment and Corporate Governance Division.
The DMDF shall be responsible for coordinating, formulating, and monitoring macroeconomic policies and programs. It shall be the main coordinating agency for economic policies and shall advise the government on macroeconomic and public finance management policies. It shall deal with all matters relating to macroeconomic surveillance and fiscal policies such as resource mobilization, expenditure envelope, public debt management, capital market development, and relations with bilateral and multilateral financial institutions. All related macroeconomic mandates will be consolidated under the Department to ensure the coordinated and efficient management of the country’s economy.
DMDF is the secretariat to the Macroeconomic Framework Coordinating Committee (MFCC). MFCC comprises various agencies, including the Royal Monetary Authority, the Ministry of Natural Resources and Energy, the Ministry of Industry, Commerce, and Employment, the National Statistical Bureau, and the Cabinet Secretariat. Through this committee, DMDF forecasts macroeconomic indicators, conducts economic surveillance, and proposes policies for sustainable economic development.
The DMDF shall liaise and coordinate with the Royal Monetary Authority on technical and analytical matters arising from the macroeconomic framework, ensuring
consistency between the fiscal and monetary policy objectives and effective policy coordination. Furthermore, the Department shall oversee the oversee the ownership interests of the government in State Enterprises
Mandates
DMDF shall shoulder very important responsibilities and support the Ministry of Finance in fulfilling its mandates as enshrined in the PFA 2007 and the Amendment 2012. The Public Finance Act, 2007 & amendments therefore mandate the MoF to:
- Coordinate government macro-economic policies and report on the state of the economy and fiscal position of the Government;
- Constant surveillance of the macroeconomy, timely research, and proposal policies for sustainable and resilient economic development;
- Coordinate the Macroeconomic Framework Coordination Committee (MFCC) to ensure the timely coordination of government macroeconomic policies and the publication of relevant data;
- Coordinate macroeconomic and fiscal responsibilities, including borrowing, on-lending, and grants, while ensuring that resources are efficiently mobilized and allocated; and
- Oversee the ownership interests of the Government in State Enterprises.
Key functions
- Lead the formulation and planning of macroeconomic management policies for the nation, primarily through the coordination and development of the medium-term macroeconomic framework and long-term models;
- Coordinate and harmonize key economic sector policies to ensure sound and cohesive economic management across government;
- Determine resource envelope and provide indicative financing for Five-Year Plans and Annual Budget Preparations, supporting effective resource allocation;
- Conduct comprehensive macroeconomic surveillance, economic modeling, and risk assessments to prescribe robust policy responses and strategies that address potential structural and policy vulnerabilities, including climate change risk;
- Advise and recommend evidence-based policies and proposals on economic and fiscal matters to support sustainable economic growth and stability;
- Ensure public debt remains sustainable by contracting at low costs and within prudent risk parameters, including preparing debt threshold recommendations based on rigorous debt sustainability analysis and medium-term debt strategies;
- Mobilize and allocate resources efficiently in collaboration with development partners, enhancing fiscal space and supporting national development priorities;
- Establish, oversee, and guide State Enterprises while promoting strong corporate governance practices and performance excellence, and ensure that SOEs contribute to sustainable economic growth;
- Engage and represent the Government in national, regional and international economic forums, fostering partnerships and knowledge exchange on economic issues;
- Serve as a secretariat to the Macroeconomic Framework Coordination Committees (MFCC) and lead the Macroeconomic Framework Coordination Technical Committee (MFCTC), ensuring informed and integrated macroeconomic policy decisions.
Structure of DMDF
Organogram
As per its mandates and functions, the DMDF is structured to have three divisions, namely;
- Macro-Fiscal Policy Division;
- Development Coordination and Debt Management Division; and
- Investments and Corporate Governance Division.
The divisions under the Department will have specific roles and functions. The Divisions will be further delineated into sections to ensure proper division of roles and responsibilities and to perform efficiently.
The Macro-Fiscal Policy Division will be further segregated into the following sections:
- Research and surveillance (R&S) sections
- Timely surveillance of the economy
- Growth accounting and productivity analysis
- Conduct research on various topical issues for informed policy guidance
- Forecasting
2. Modeling, innovation and machine learning (MIML) section
- Macro Economic and econometric Modeling (MEF, CGE, OLG, EEWS and others)
- Machine learning and big data (large models and other innovative ways to forecast leading economic indicators,
- such as satellite imagery) including their incorporation into macroeconomic modeling
- Quantifying Macro effects of climate and environment policies
- Forecasting
3. Economic and fiscal policy evaluation section
- Macroeconomic Policy review and analysis
- Evaluating and stimulating policies
- Forecasting.
The following sections will support the Development Coordination and Debt Management Division:
- International Cooperation, Development and Policy Coordination Section (Front Office);
- Debt and Grant Analysis and Strategy Formulation Section (Middle Office); and
- Debt and Grant Information Management and Payments Section (Back Office).
The Investment and Corporate Governance Division will have the following sections:
- Performance Management Section;
- Corporate Finance & Investment Management Section; and
- Corporate Governance & Monitoring Section.