Vision
Contribute to nation building through the development of an effective revenue system.
Mission
To ensure that the Tax and Customs administration has the capacity to collect taxes efficiently and effectively at minimum cost through impartial and consistent enforcement of regulations, and to provide a convenient and honest service to the taxpayers.
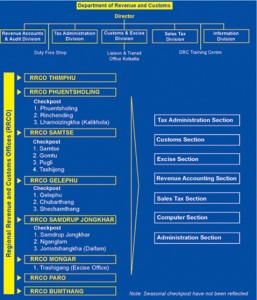
Organisation Chart
Divisions
Tax Administration Division
- Implement and monitor the Income Tax Act of the Kingdom of Bhutan, 2001 and the Rules.
- Review and advise the Ministry of Finance on all revenue related matters, tax policy and planning.
- Revision of legislation, etc. from time to time.
Customs and Excise Division
- Implement and monitor the Sale Tax, Custom and Excise Act of Kingdom of Bhutan, 2000 and the Rules.
- Review and advise the Ministry of Finance on Custom and Excise policies.
- Coordinate with other law enforcement agencies in prevention of the smuggling of restricted and prohibited goods.
- Process Excise Duty Refund claim from Government of India.
- Liaise with WCO, Regional Custom Administration and other international agencies.
Revenue Audit and Accounts Division
- Assessment, collection and deposit of national revenue.
- Investigate revenue irregularities.
- Advice and interrupt the rules and procedures in revenue matters to revenue agencies.
- National revenue forecast on fiscal year basis as well as for the plan period.
- Produce the national revenue report.
- Process refund from the government revenue account.
Sales Tax Division
- Implement and monitor the Sales Tax, Customs and Excise Act of the Kingdom of Bhutan, 2000 and the Rules.
- Review and advise the Ministry of Finance on policy planning and revision of rules/procedures.
- Issue and monitor Sales Tax Exemption (STEC) on plants, machinery, spare and raw materials etc.
- Refund of Sales Tax.
Information Division
a. Public Information Services
Dissemination of direct and indirect tax information, rules and regulation.
b. IT Section
Develop and maintain IT systems for effective and efficient management
Taxation System
Historical Background
Before 1960:- Taxes were collected in kind and in form of Labour contribution. Taxes in kind were gradually phased out to be replaced by nominal monetized tax on:
- Land
- Property
- Business income and
- consumption of good and services
First Major Tax Reform in 1989
Purpose:
- To take stock of various tax measures
- To develop a coherent and rational tax system
- To establish a system of tax in fair, equitable and efficient manner that minimises the need for frequent change.
- To fully document the system in a way that promotes tax payer awareness
Main features:
- BIT on net profit replaced 2% turnover tax
- Export income exempted
- Plant machinery exempted from sales tax and import duty
- other nuisance taxes were abolished
Tax Reform in 1992
Purpose:
- Rationalisation of tax structure
- Expansion of tax base
- Simplification of administrative procedures for compliance and transparency
430,614 total views, 30 views today